Introduction#
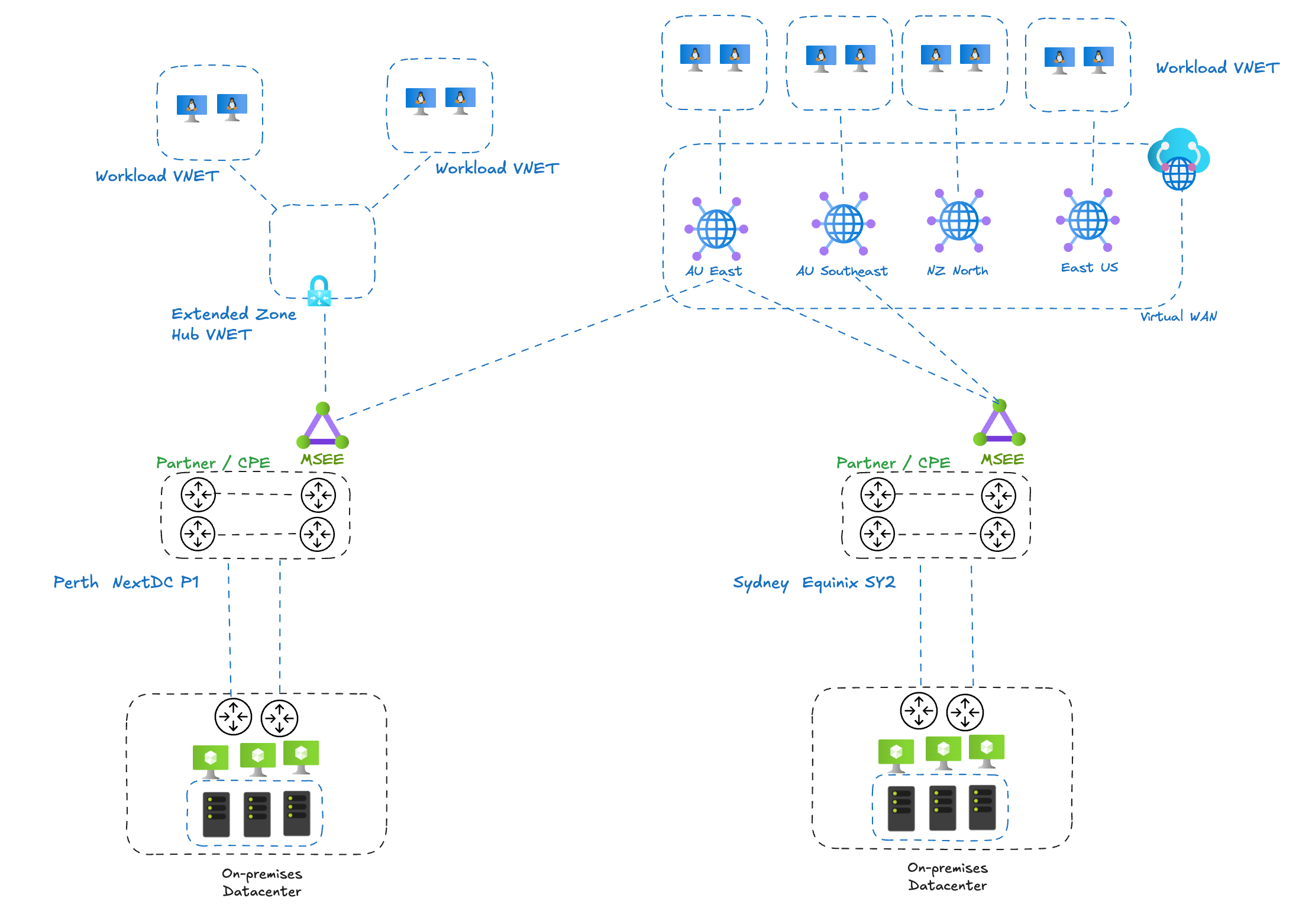
This blog post shares an engineering validated pattern for establishing connectivity between Azure Extended Zones and Azure Virtual WAN environments. Currently, Virtual WAN hubs cannot be deployed within Extended Zones, so we need alternative approaches to bridge these environments.
Below is a summary of connectivity options for Extended Zone
Connectivity Options for Extended Zones#
| Customer Scenario | Approach |
|---|---|
| Customer with Traditional Hub & Spoke VNet and looking to connect to Azure Region (eg Azure AU East) | Utilise Global VNet Peering for connecting from Extended Zone to Azure Region |
| Customer with Traditional Hub & Spoke VNet and connect to on-premises (using Perth Edge) | Utilise ExpressRoute Connectivity or SD-WAN / VPN Connectivity using Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) |
| Customer with Virtual WAN and looking to connect to Azure Region from Extended Zone (eg Ex Zone Perth -> Azure AU East) | Create Traditional VNet Hub & Spoke pattern in Extended Zone and utilise ExpressRoute Circuit for connectivity to Virtual WAN hub in Azure Region |
Supported Networking Services for Extended Zones (Sept-2025)#
- Virtual Network
- Standard Public IP
- Standard Load Balancer
- ExpressRoute Circuits and ExpressRoute Gateways
- Virtual Network Peering (Local and Global)
- Private Link
- Virtual Network Appliances (NVAs)
Services that are currently not available (Sept-2025)#
- Virtual WAN
- VPN Gateway
For this blog post, we’ll cover 3rd scenario where a customer already has Virtual WAN environment and looking to establish connectivity to Extended Zones
Configuration#
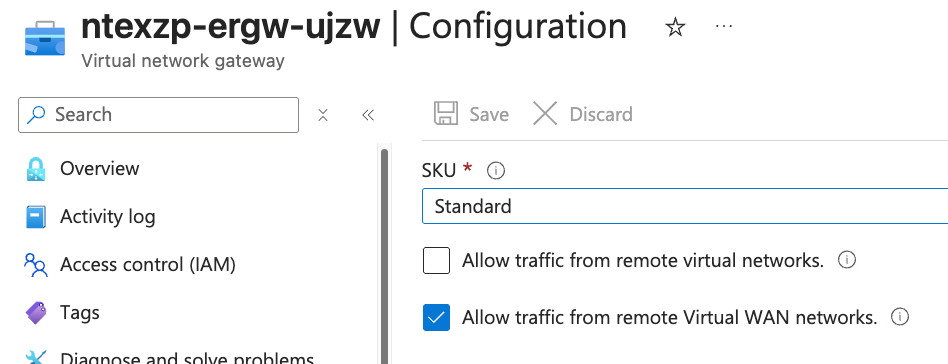
This setup follows the same configuration pattern used for establishing coexistence between Hub-Spoke environments and Virtual WAN. The key requirement is enabling bidirectional traffic flow between the two gateway types.
Essential Configuration Settings:
- Hub-Spoke ExpressRoute Gateway: Enable “Allow traffic from remote Virtual WAN networks”
- Virtual WAN ExpressRoute Gateway: Enable “Allow traffic from non Virtual WAN networks”
Below is my ExpressRoute Gateway deployed to Extended Zone VNet.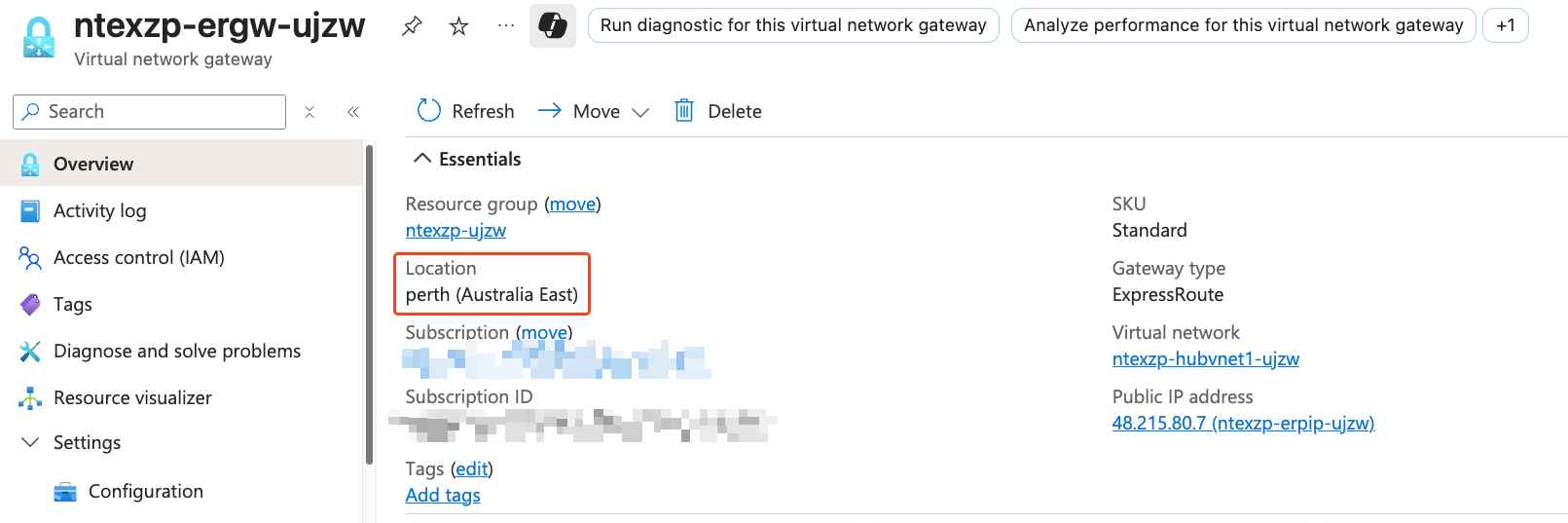
Validating Connectivity#
Step 1: Verify Extended Zone VM Routes#
First, validate that VMs in the Extended Zone are learning routes from the Virtual WAN environment through the ExpressRoute Gateway.
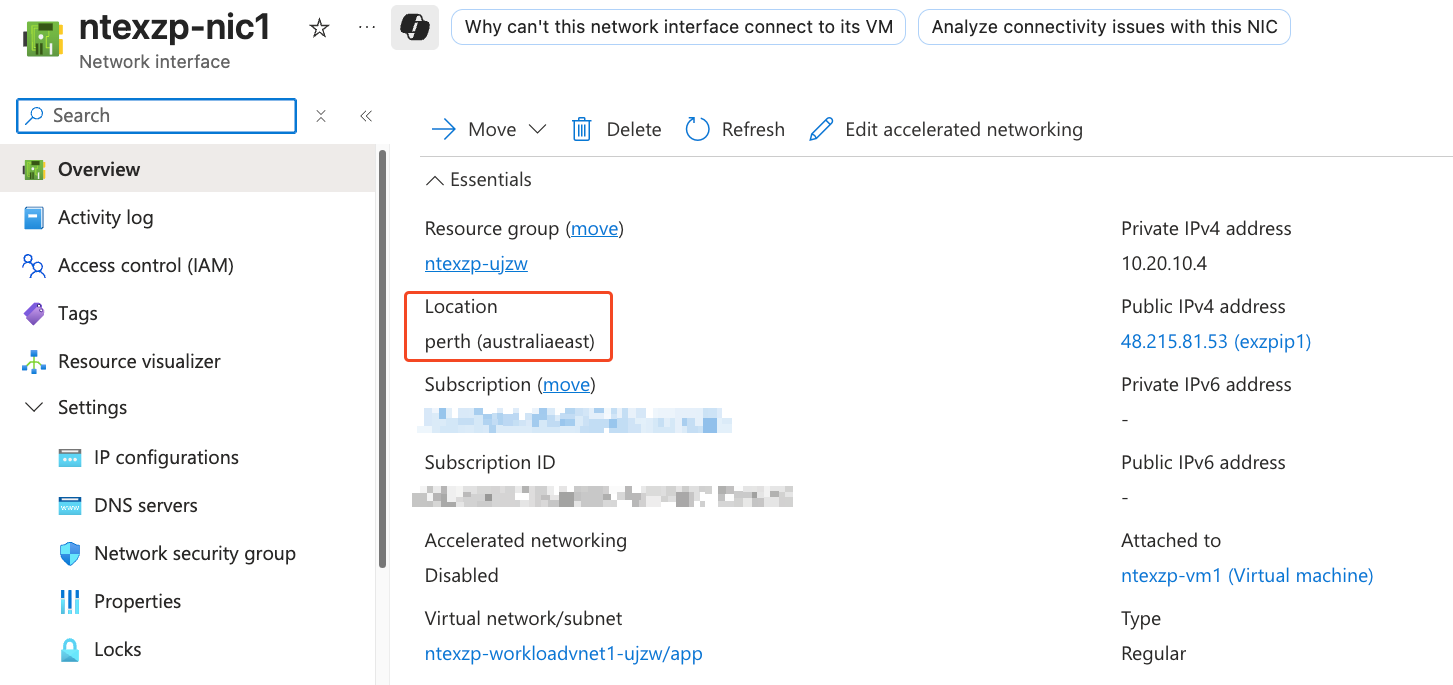
Effective routes from my VM in Perth Extended Zone show routes learned from ExpressRoute Gateway and these are remote routes from my Virtual WAN environment.
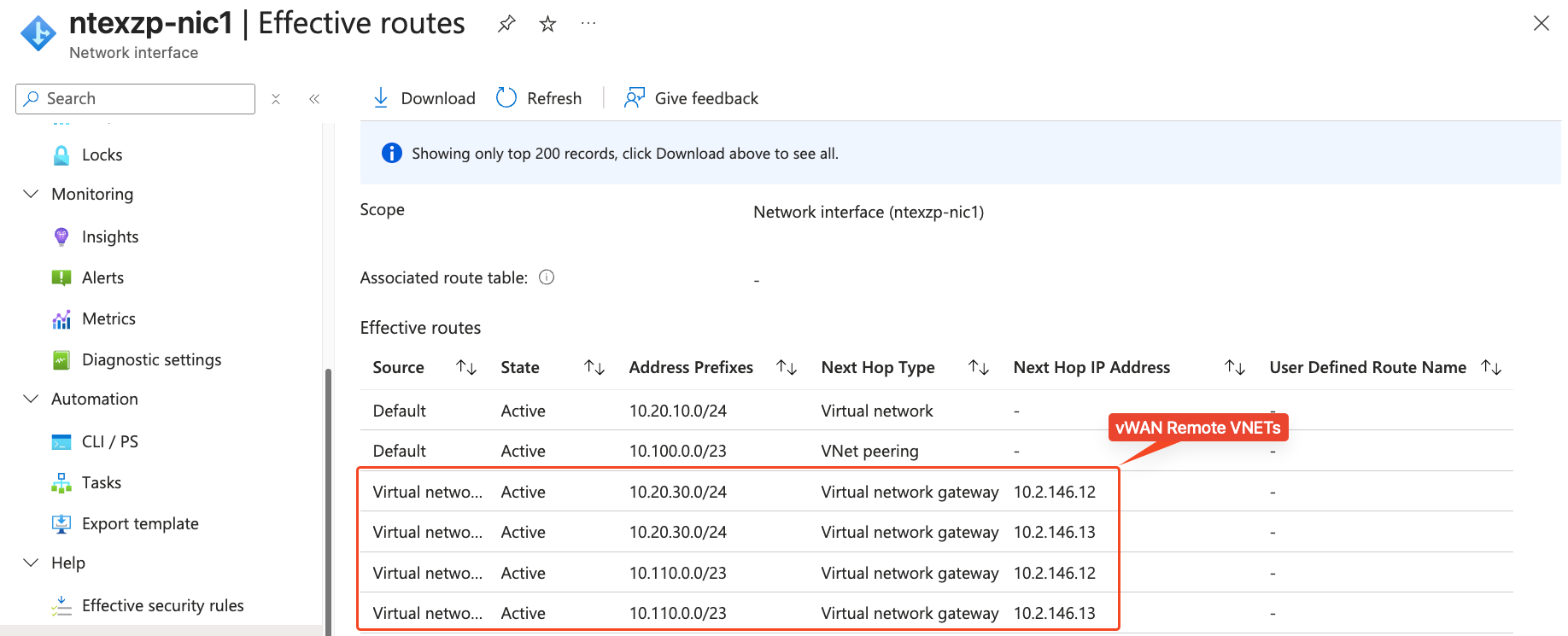
Step 2: Validate Virtual WAN Environment Routes#
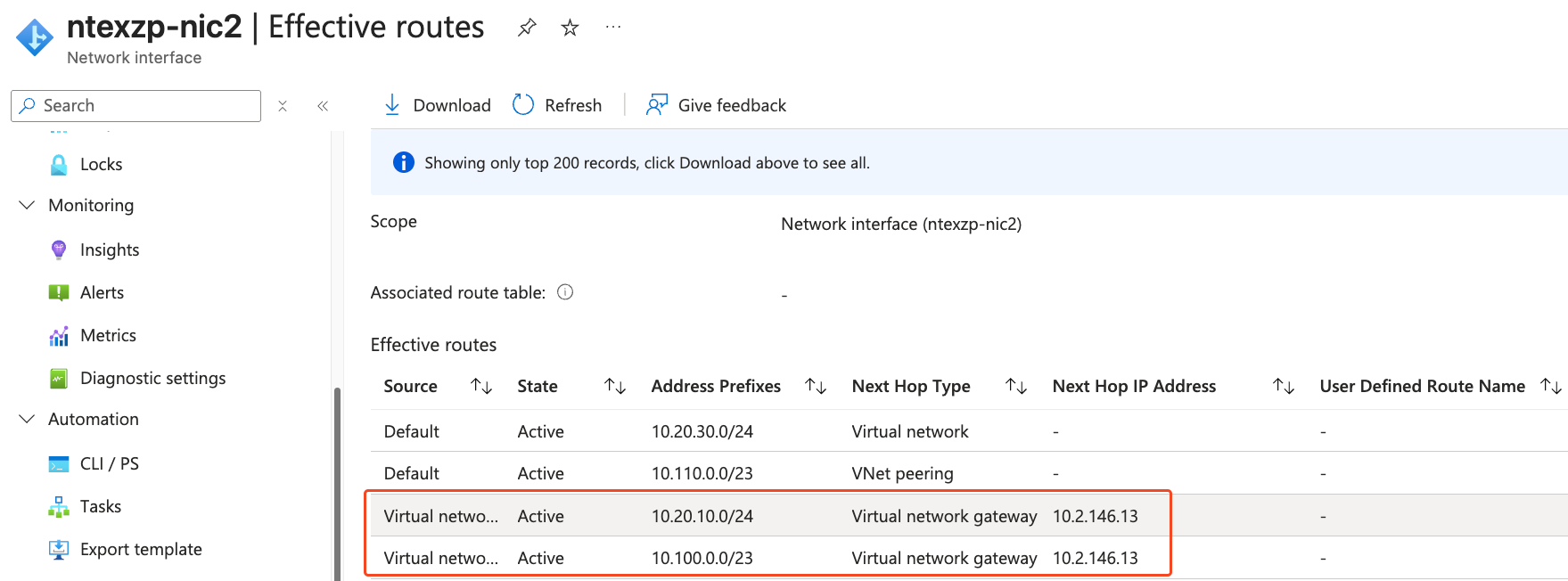
Next, verify that VMs connected to the Virtual WAN hub are learning Extended Zone VNet prefixes.
Below routes are learned by my virtual machine connected to Virtual WAN hub that is hosting ExpressRoute Gateway and we are able to see Extended Zone VNet prefixes are learned by the network interface attached to my VM.
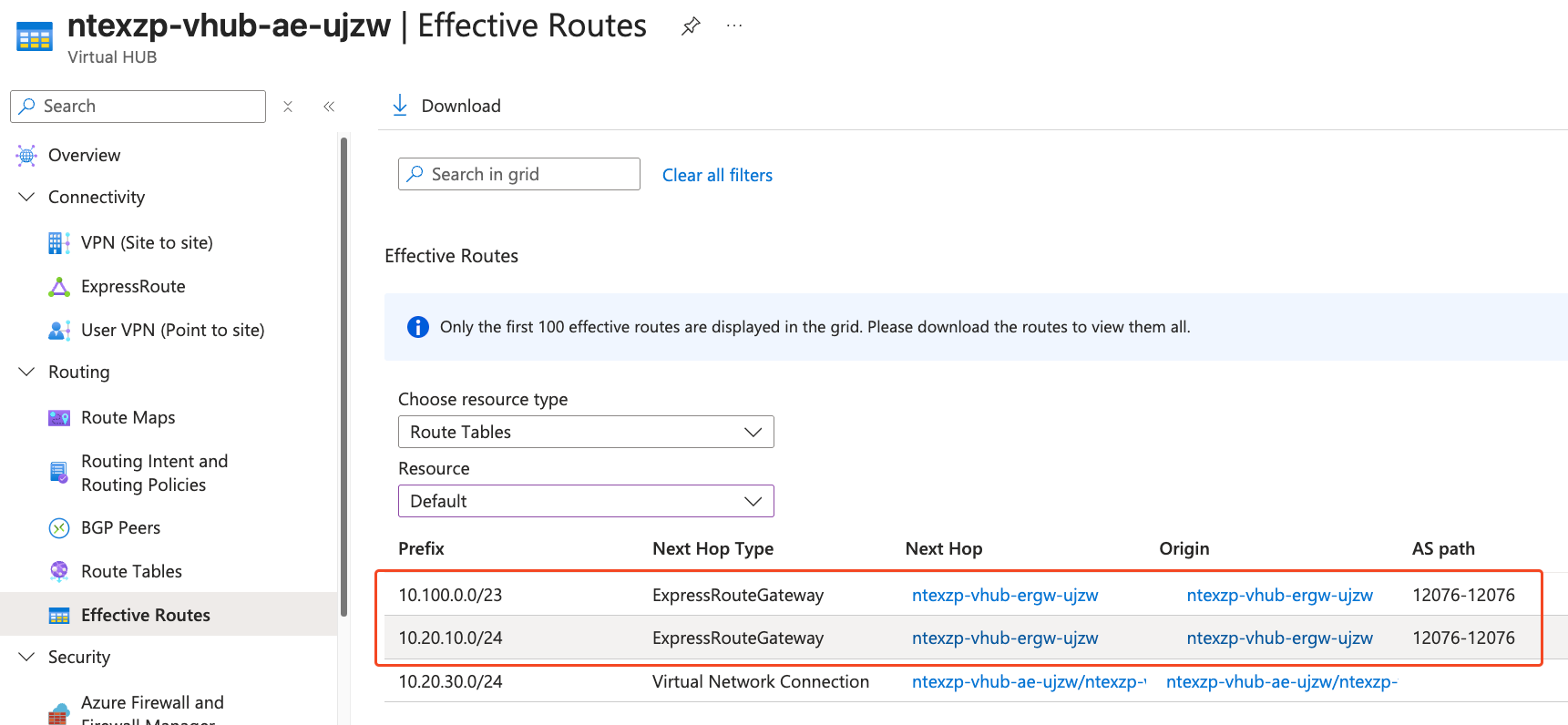
Step 3: Check Virtual WAN hub Effective Routes#
For deeper insight into routing behavior, examine the effective routes from the Virtual WAN hub. This view helps understand:
- AS Path information
- All prefixes learned by the ExpressRoute Gateway
- Route propagation between environments
Additional Considerations#
Bandwidth Constraints: ExpressRoute Gateway bandwidth is limited by the gateway SKU configuration
Additional Latency: The gateway hop introduces additional latency to traffic flows between environments
Conclusion#
If you are already using Virtual WAN network deployment, you can now take full advantage of Extended Zones by connecting to your existing Virtual WAN environment using your current ExpressRoute connectivity.
